CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING THE SEARCH FOR RESERVE CAPACITIES OF THE SPORTS MASTERY IMPROVING IN HIGHLY QUALIFIED CYCLISTS
Author: Aleksandr Petrovich Yablunovskiy,
Doctor in sports medicine
BACKGROUND
Having some experience in professional cycling, I would like to share my observations from the perspective of the team doctor about the possibilities of applied kinesiology that can significantly affect the health of athletes and improvement of their skills.
Further development of physical fitness and sports in our country has been elevated to the rank of the state’s priority task, requiring involvement of 70% of the population into physical fitness and sports, and in high-level sport – return to the top three of the strongest sports nations in the world.
Health disorders and diseases, especially of the cardiovascular system, are the main reason for temporary or permanent withdrawal from sports. And the cases of sudden death of athletes during competitions prompted the adoption of new laws that expanded and tightened the medical control of people involved in sports.
Due to the increasing level of records that exceed the capabilities of the human body, all top-level athletes are required to undergo an extensive medical examination (EME) 2 times a year with admission to competitions. New victories require the search for reserve opportunities and, of course, without compromising the health of athletes.
In the theory of sports, the supercompensation model is the generally accepted explanation of the biological effect of the fitness improvement.
It is well known that muscles with normal tonus are trained and recovered adequately. But if, for some reason, the muscles have become hypotonic, then even normal physical activity can become excessive and will require more time for recovery. The balance between the amount, intensity of physical stress and the space for recovery is precisely the art of coaching, which allows you to smoothly bring an athlete to the peak of physique. Increased stresses and underestimation of the recovery importance lead to physical exertion, overtraining, injuries and illnesses. But in order to get the coveted admission, without which participation in the training camp is not funded, most athletes refrain from minor complaints when undergoing the EME. Only identification of significant deviations in analyses and tests allows you to find an illness and perform treatment on time. In case of minor deviations, the decision is made on an individual basis. Idiopathic scoliosis and autonomic dysfunction syndrome are quite common diagnoses among cyclists. The team doctor in the “field conditions” is charged with carrying out therapeutic and preventive measures with the obligatory implementation of the specialists’ recommendations. As a rule, these recommendations are general in nature: normalization of physical stresses, ensuring adequate recovery, exercise therapy, massage, hydrokinesiotherapy. And since the reserve capabilities of an athlete directly depend on the effectiveness of limiting factors elimination, the chain of cause-and-effect relationships, leading to scoliosis and various kinds of autonomic dysfunctions, is not always obvious to the team doctor, especially in symmetrical sports.
The objectives of this study were:
– Evaluate the effectiveness of applied kinesiology diagnostic and therapeutic methods on sports achievements improvement in the men’s team pursuit on the track.
– Evaluate hardware nonlinear diagnostics capabilities in 3D visualization of a pathobiomechanical disorders chain, that leads to development of limiting dysfunctions of organs and system in highly qualified athletes.
STUDY MATERIAL
The study involved 12 highly qualified athletes approved for professional sports activities according to the results of the EME. All of them were racers of the same club and competed in one of three age categories: juniors, juniors-“unders” and men-elite. Juniors had the title of Master of Sports, “unders” and men – Masters of Sports of International Class. In “team pursuit” all cyclists were the best in Russia, had victories at the junior European and World Championships. The race is competition between two teams that start on the opposite sides of a track, lap length is 4 km. The training methods, sports equipment, natural gift, accommodation and food conditions were the same. The study took 2 years, starting from February 2019.
Many cyclists are well aware of deviations in their posture. These minor signs are: an asymmetric seat on a bicycle, especially at the end of a race with the development of fatigue; registration of the asymmetry of forces application of on a pedal by a strain gauge; different muscle mass of the hips and shins.
In recent years, a lot of gadgets have appeared in bicycle equipment that allow you to register the main important indicators directly during training and racing. This helps the coach to analyze, determine the optimal training plan and monitor the work done.
As an example, the protocol for monitoring the mountain stage of a race is presented. The asymmetry indicator of the force application on a pedal, which was 45/55%, is highlighted in red. But many racers believed that there was no resulting loss of power, since the “leading” leg only compensated for the “non-leading” one. Coaching recommendations are mainly consisted of additional training of the latter.
DIAGNOSTICS METHODS
All athletes underwent visual, manual diagnostics, manual muscle testing according to the accepted methodology with an assessment of the step pattern and the activity of unconditional primitive reflexes, provocative kinesiological tests.
Some cyclists expressed skepticism about of weakness during the test. I think that many kinesiologists have had to deal with this phenomenon. Due to the limited free time, frequent muscle testing is not perceived with pleasure by all riders. Understanding comes only when pain symptoms appear.
That is why for screening of organ pathologies, infections, vitamin and mineral deficiencies, food allergens, I used a licensed apparatus “Metatron” with “Metapathia Clinical” software and 4.9GHz non-linear sensor, developed by the Institute of Practical Psychophysics.
Unlike the Voll’s electropuncture diagnostics method, when energy potential of organs is evaluated via biologically active points, we performed evaluation of organs condition directly by means of the resonant amplification of the evaluated organ’s signal and contactless reading of data with use of trigger sensors.
During the study study, the functional state of tissues is evaluated by their chromogenicity on the Fleindler color scale, from optimal regulation level to decompensation of adaptation mechanisms.
A retrospective analysis of the EME of these athletes, obtained from the results of clinical analyses, various kinds of biochemical analyses, functional diagnostic studies (ECG, echocardiography, US of internal organs, fluorography, computer spirometery, bicycle ergometry until failure to continue) and examinations by 12 specialists physicians, was also carried out.
STUDY RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The reason for suboptimal statics and dynamics, according to modern concepts, is the asymmetry of postural muscle tonus resulting from dysfunction of any sensory inputs of the postural system.
Cycling position of an athlete on a bicycle itself can contribute to development of a dysfunction.
Such suboptimalities of the step pattern are: fixed feet and shoulder girdle, enhanced lordosis of the cervical spine and smoothed lordosis of the lumbar spine, labored abdominal breathing. Due to the discrepancy between the professional pedaling pattern and the running pattern, cyclists do not like and intuitively do not include jogging and cross-country run in their general physical training.
This kinesiological study revealed the presence of regional asymmetry, compression syndromes, autonomic dysfunction and pathological activity of visceral motor reflexes and unconditional primitive reflexes in all cyclists.
The most significant of them for cycling was the palmar grasp reflex, since it is caused not only by the classic irritation along and across, but also by closing the fingers, as when holding a steering wheel. I think this may also be relevant for other sports where you have to hold something in your hands.
Thus, visceromotor and primitive reflexes created descending dysfunction. A flat foot, trigger points in the leg muscles, as a result of overtraining of the muscles, formed an ascending dysfunction with displacement of the talus bone, instability of syndesmosis of fibula and shin bone heads, TMJ, C0-C1. As a result, each of the examined athletes had their own “vicious circle” of limiting dysfunctions.
According to the EME conclusions, all athletes had from 3 to 8 diagnoses. The most frequent among them were: flat foot in 100% of athletes; idiopathic scoliosis in 83.3%; autonomic dysfunction syndrome or hypertensive reaction to exercise in 83.3%; biliary dyskinesia, Gilbert’s syndrome in 41.6%; allergic manifestations (atopic asthma, dermatitis, rhinitis) in 41.6%; chronic tonsillitis in 25%.
The results of kinesiological and hardware diagnostics confirmed the presence of pathologies in these organs. In addition, 50% of athletes were tested for giardia, amoebae or ascaris. Unfortunately, the EME standard does not include tests for the presence of protozoal infection and helminths. The high frequency of parasitic invasion and chronic inflammatory conditions in cyclists is often associated with getting road dirt on the face during training or competitions in the rain.
As an illustration of the biochemical component importance in such cases, I will give a clinical example of how the Hippocratic oath helped a foreign rider become a world champion. For many years of working in professional cycling, team personnel are well acquainted with each other. I was asked to consult a well-known foreign racer who had a lower back pain during the races for 3 months, power and efficiency decreased. He was examined by all possible classical methods. Osteopathic treatment, manual therapy, massage had short-term success. Testing revealed the presence of ascariasis and food allergies to some products. The doctor of his team was surprised by the methods he saw, did not object to treatment with pyrantel, but only after the end of the multi-day race. The rider insisted on immediate treatment. With each stage of the race, his condition improved, he finished it well. After that there was the Grand Tour of the Vuelta a Espana, where he won 2 stages. And then he won the World Championship with a big lead and gave me a firm handshake.
The chain of pathobiomechanical disorders is visualized well by the “Metatron” device.
As a typical example, images of the same athlete before and, for comparison, after correction are presented.
The imbalance in the tonus of the neck muscles and extensors leads to an asymmetric pull at the occipital bone, causing displacement of the temporal bones and compression of the vagus nerves in the jugular foramen of the skull with a subsequent disorder of the vegetative provision of internal organs and the development of visceral dysfunctions:
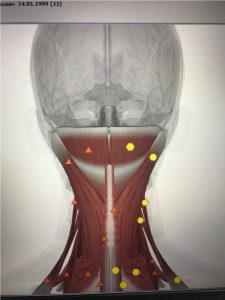 |
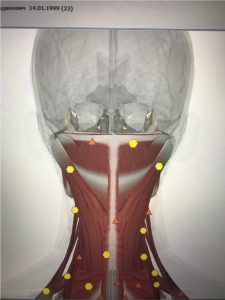 |
| Pic.1 Asymmetric neck muscle tonus | Pic. 2 After correction |
The imbalance of the neck muscles tonus leads to instability of the intervertebral discs and subluxation of the cervical vertebrae.
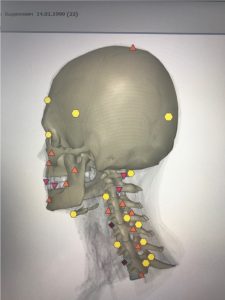 |
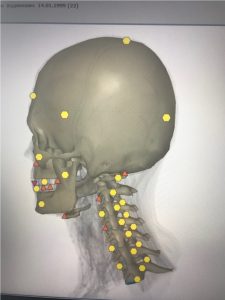 |
| Pic. 3 Instability of vertebrae and disks | Pic. 4 After correction |
The instability of C0 – C1 creates conditions for irritation of the vertebral artery with a cerebral hemodynamics disorders at maximum physical stress.
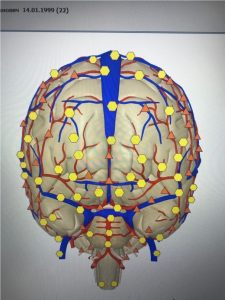 |
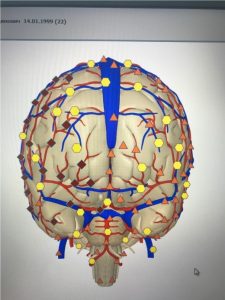 |
| Pic.5 Vessels at rest | Pic.6 Blood flow asymmetry in 20 minutes after a race |
The unstable position of the C3-C5 vertebrae causes compression of the diaphragmatic nerves with the development of dysfunction of the thoracic diaphragm. When hypotension of the cupula occurs, auxiliary muscles are actively involved into respiration biomechanics, especially the crura of diaphragm, which compress the nerves of the upper lumbar plexus.
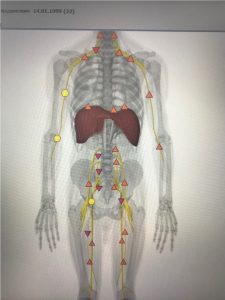 |
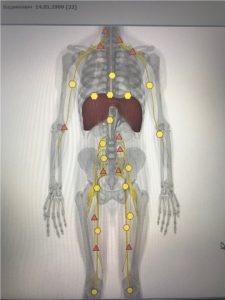 |
| Pic.7 Weakness of cupola and compression of lumbar plexus by the crura of diaphragm | Pic.8 After correction |
Hypotonic cupolas of the thoracic diaphragm cannot withstand intra-abdominal pressure and rise upwards. This condition leads to compression of the cardiac sac and restriction of heart mobility, especially with maximum physical stress.
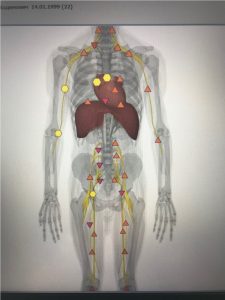 |
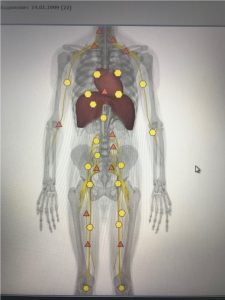 |
| Pic.9 Compression of the cardiac sac by cupolas | Pic.10 After correction |
Asymmetric compression of the upper lumbar plexus causes weakness of the corresponding muscles of the pelvis and lower extremities, forming instability of the lumbar region, pelvis and torsion.
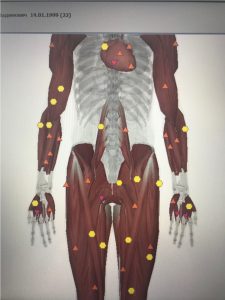 |
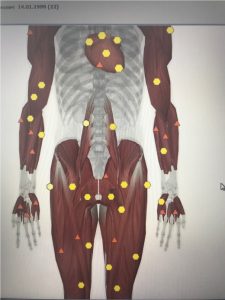 |
| Pic.11 Torsion imbalance of a muscle tonus | Pic.12 After correction |
When an athlete perceives the results of a hardware study with distrust, conducting a muscle test and his own feelings help him to assure himself that the diagnosis is correct. These two methods complement each other, since their results coincide.
TREATMENT
The program of therapeutic and restorative measures covered the impact on the most significant mechanisms of dysfunction:
– Treatment of parasitic infestations, correction of deficiency of vitamins, minerals and nutrients;
– Manual correction by various kinesiological methods, periodically and immediately before a competition;
– Training in regular self-treatment of painful trigger points and cohesions muscles by the method of ischemic compression using a percussion massager, kinesiological rollers and balls;
– Avoiding of food allergens and products that caused reflex muscle weakness, while maintaining caloric content and balanced diet;
– Training in self-correction of pre-start emotions.
As a result of this therapeutic and restorative program, the number of functional disorders decreased, in accordance with the findings of the EME.
The main criterion for the effectiveness of the chosen methods of diagnosis and treatment was the dynamics of the sports skills improvement, which is presented in this graph.
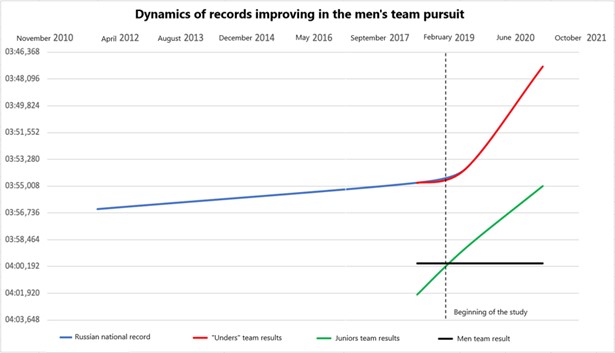 |
| Pic. 13. Dynamics of Russian national record improvement in the men’s team pursuit in 2011-2021 |
Since 2011 and before the study, the relative improvement rate of the Russian record was 0.25 seconds per year on average. During the study period, the team of “unders” improved it by a factor of 14. An improvement of 7 seconds in 2 years. This is exactly a half of a lap. That is, in the virtual pursuit race, they caught up with themselves. This allowed the “unders” not only to confirm their leadership at the European and World Championships in their category, but also to win the European Games 2019 and the European Championship 2020 in the adult category. The same dynamics of sports skills improvement was shown by the junior team, catching up and surpassing the men’s team in its skill. In the men’s team, the reasons for the lack of growth in sports results were: greater number of diagnoses than in juniors, reduced discipline in self-treatment of muscle trigger points and compliance with recommendations for proper nutrition.
CONCLUSIONS
- Use of applied kinesiology and NLS-diagnostics methods in the practice of a sports doctor allows to identify the causes of diseases and dysfunctions quickly and with a high degree of reliability, effectively eliminate them, helping to achieve the growth of sports mastery;
- Potentials of NLS-diagnostics help a team doctor in visualizing a chain of cause-and-effect relationships of limiting dysfunctions and promptly monitor the results of their correction;
- Performance improvement in the high-level sports is a complex multifactorial process that requires an integrated approach and strict implementation practices by athletes;
- Considering its high efficiency, I suggest that employers, in order to stimulate sports medicine doctors to study applied kinesiology, add to their qualification requirements a provision not only about knowledge, but also the ability to conduct a functional muscle test.
REFERENCE LIST
-
3D computer NLS-graphy: Collection of works / Edited by V.I. Nesterov. – М.: “Izdatelstvo “Prospekt” LLC, 2012.
-
L.F. Vassilyeva, A.M. Mikhailov. Manual diagnostics and therapy of internal organs dysfunctions. – Novokuznetsk: Poligrafkombinat, 2002.
-
L.F. Vassilyeva, O.V. Kuznetsov, A.Yu. Mochalov. “Muscle-fascial links”, Guidance materials for students. Moscow. 2009.
-
G.A. Ivanichev. Painful muscle knots. – 1997.
-
D. Liv. Materials of “Applied kinesiology in sports medicine” conference – Moscow, 2010.
-
M.R. Mogendovich. Motor-visceral and visceromotor reflexes. Perm, Nauka, 1963
