P.MacAdam, L.Birch, S.Carryngton
London Bridge Hospital
INTRODUCTION
Prostate abscess is not frequent, but serious complication of an acute prostatitis or an aggravation of a chronic prostatitis. According to various authors, prostate abscess is registered in 5-8 % of prostatitis patients. The abscess develops because of inadequate treatment of an acute prostatitis in the patients who were subjected to catheterization, transurethral drainage of bladder, suffering from diabetes or being in an immunodeficiency state.
Abscess diagnostics at a formation stage is difficult. Earlier a priority in diagnostics belonged to a clinical data and results of digital rectal examination. It complicated early revealing of the disease. So, according to the references, prostate abscess is diagnosed only in 0.2%-1.4% of patients with clinical urological semiology and in 0.5-2.5% of cases in patients with semiology of prostate gland diseases. The reasons of difficulties with diagnostics is a development of disease along with an aggravation of a chronic prostatitis, frequent combination of an abscess with other inflammatory diseases of urinogenital system (pyelonephritis, epididymoorchitis, etc.), occurrence of the latent forms of the disease in the midst of applied antibacterial therapy, absence pathognomonic symptoms of an abscess (pain in perineum and rectum, dysuria, fever).
Three-dimensional (3D) NLS has proved itself as simple, noninvasive and highly informative diagnostics method, thanks to absence of beam loading. The issue of 3D NLS application in monitoring of conservative treatment of prostate abscess is studied insufficiently.
The purpose of this work is studying of 3D NLS with NLS-angiography possibilities in monitoring of conservative treatment of prostate abscess.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
We have carried out the retrospective analysis of examinations of 11 patients suffering aggravation of chronic prostatitis, complicated by development of prostate abscess. Average age of patients was 42.5 ± 3.7 years (27 to 51 years old). All patients were subjected to complex research including analysis of the clinical data, digital rectal examination of prostate gland, laboratory researches and NLS-research using “Metatron”-4025 device with generator frequency of 4,9 GHz, equipped with program “Metapathia GR Clinical” (Institute of Practical Psychophysics, Russia), with possibility of 3D NLS-angiography. NLS-research included two-dimensional and three-dimensional scanning, ultramicroscanning and spectral-entropic analysis (SEA) of prostate gland tissues structures. NLS-angiography was applied before treatment, then in 2 weeks, in 1 month and in 1.5 months. Our study involved patients treated with conservative methods of this disease treatment, including a course of antibiotic treatment.
Using 3D NLS-graphy we evaluated a condition of prostate gland; presence of focal zones of high chromogeneity, their spectral structure. Using 3D NLS with angiography we evaluated a condition of vessels, expressiveness of affection of a vascular wall in focal zones. 3D NLS with NLS-angiography data was compared with clinical and laboratory results.
RESULTS
On the basis of digital rectal examination prostate abscess was suspected in 4 patients, we detected: enlargement and morbidity of prostate glands, fluctuation symptom was marked. In other patients the gland was enlarged and was painful, in these cases a preliminary diagnosis was made: an aggravation of a chronic prostatitis.
At 3D NLS affection of the gland was marked in all cases. In all patients we detected presence of high chromogeneity areas (5-6 points on a Fleindler’s scale) in structure of the gland. The quantity of the areas varied from one to five: in 4 patients – one area, in 3 – two, in 2 patients – four, and in another 2 – five areas were visualized. Altogether 28 areas were revealed. The structure of 24 areas was non-uniform, of 4 – homogeneous, that complicated differential diagnostics.
Three-dimensional angiography mode detected affection of the gland’s vessels with presence of vessels affection zones in a projection of hyperchromogenic areas.
Fig. 1. NLS study. Prostate gland abscess. Two areas of increased chromogeneity are visible in a structure of the gland.
Fig. 2. Spectral-entropic analysis. Prostate gland abscess.
Dynamic observation within first two weeks of clinical treatment, laboratory analyses have registered positive changes in 9 patients. It correlated with 3D NLS data – in 4 patients a volume of hyperchromogenic areas has decreased by 0.5 sq.cm. A volume of changed areas has remained the same in other patients.
Three-dimensional NLS-angiography has visualised positive changes in 9 patients – in form of vascular channel damage expressiveness decreasing.
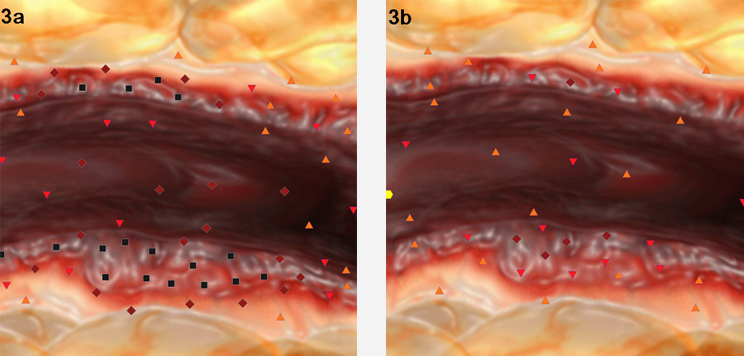
Fig. 3. UltramicroNLS-graphy mode. а. Before treatment. Hyperchromogenic areas are detected in prostate gland vessel wall. b. Two weeks after treatment start, positive dynamics is registered, previously mentioned areas are gone.
In 2 patients due to absence of positive dynamics according to results of SEA at 3D NLS with NLS-ultramicroangiography, correction of antibacterial therapy was fulfilled. At the control researches, carried out within 3-5 weeks during the course of treatment, positive dynamics in the form of normalisation of SEA results was detected in all patients. There was a gradual decrease of chromogeneity of the affected areas. The quantity of hyperchromogenic areas has decreased – to 5 (in 2 patients multiple abscess of the gland were diagnosed), their chromogeneity was lower in comparison with the previous researches. In patients with remaining abscess formation areas, complete disappearance of such areas happened in 6 weeks from the start of treatment. Research in a three-dimensional NLS-angiography mode has shown in most cases gradual restoration of a vascular channel in a projection hyperchromogenic zones after treatment.
DISCUSSION
The abscess of prostate is difficult to diagnose, because the semiology is not strictly specific. More often symptoms of an abscess, an acute prostatitis and an aggravation of a chronic prostatitis are identical. Only in several patients the classical combination of fever, dysuria, urinations frequency increasing, pain in perineum and bacteriuria is marked. So, the fever in patients is marked in 60% – 75% of cases, pain in perineum – in 20% – 33% of cases. Presence of a fluctuation symptom at palpatory study is registered not often also – in 27% – 35% of cases and corresponds to a purulent-destructive stage. In laboratory researches of prostate gland secretion the acute increase of leukocytes quantity is noticed, that is also typical for acute prostatitis. The invaluable help in diagnostics of prostate gland is rendered by SEA results.
In our research in patients the most frequent symptoms before treatment were a fever (in 8 patients) and urinations frequency increasing (in 7 patients). The fluctuation symptom has not been revealed. In all patients prostate gland secretion analysis has revealed essential increase of leukocytes quantity.
According to references, there are two stages in abscess development – infiltrative stage and purulent-destructive stage. NLS-picture infiltrative stage in 3D NLS mode is characterized by presence of hyperchromogenic zones of oval shape, of homogeneous and non-uniform structure. At inflammatory reaction progressing in a structure of the gland hyperchromogenic areas of non-uniform structure appear. At formation of an abscess structure of the areas becomes more homogeneous. The first stage is reversible and is a subject of conservative treatment. The second stage is irreversible, and surgical treatment is required here.
According to our research, in all patients the disease has been revealed in its first stage. It was promoted by several factors: evident clinical picture, carried out laboratory research taking into account availability of program for NLS-screening of prostate gland diseases, that provided early admittance of patients and dynamic supervision over a treatment course.
Differential diagnostics of an abscess at NLS is carried out with cysts and with rostate gland cancer sites. Simple cysts and cystic degeneration of prostate gland are sonographically similar to developed prostate abscess, but differ in location (more often: a single central location at congenital cysts or location in the central part against the background of adenomatously changed parenchyma). It is difficult to differentiate an abscess and cancer of prostate gland. Distinctive criteria at NLS are considered to be: location – an abscess is more often located in a transitive zone of a gland, but cancer – in peripheral; size – more often an abscess is larger than a tumor, at an abscess – presence of changes in structure and size at dynamic treatment. In diagnostically difficult cases SEA of prostate gland is recommended. In our opinion, location and size are not the exact diagnostic criteria: in the presence of large tumors a cystic component may be present in their structure, which is a site of disintegration. In 8 patients of our research, abscess formation sites were located in a peripheral zone, and the average size of them was small – comparable with a tumor site.
Dynamic observation during a small period of time has shown that tumor sites and cystic degeneration areas do not change in structure and size; abscess formation sites, in case of a positive response to therapy decrease in size, when they disappear formation of small fibrous sites in a projection of these sites is possible.
In our research within the first two weeks (10-14 days) in 9 patients we marked reduction of abscess formation sites after applied therapy, three-dimensional NLS-angiography has shown positive changes in a vascular wall condition in 9 patients. In 2 cases because of positive dynamics absence, a correction of antibacterial therapy was done.
Disappearance of abscess formation sites in all patients was noted in 6 weeks after initiation of treatment, at the same time in structure of 2 sites we noted formation of small fibrous sites.
Thus, 3D NLS with NLS-angiography is an informative method of prostate abscess conservative treatment monitoring an in out-patient conditions.
REFERENCES
1. Barozzi L., Pavlica P., Menchi I., De Matteis, Canepari M.Prostatic abscess: diagnosis and treatment. // AJR., 1998, March, 170: pp. 753-757.
2. Kravchick S., Cytron S., Agulansky L., Ben-Dor D. Acute prostatitis in middle-aged men: a prospective study. // BJU Int. 2004 Jan; 93(1): pp.93-96.
3. Lee F Jr., Lee F., Solomon M.H., Staub W.H., McLeary R.D. NLS-graphic demonstration of prostatic abscess. // J. Ulytrasound Med. 2012; 3: pp. 121-123.
4. Slojewski M.,Czerwinski F.,Sikorski A. Microangiographic imaging of the prostate.// BJU Int., 2009; 89: pp. 716-718.
5. Wasserman N.F. Prostatitis: clinical presentations and NLS-graphic findings.// BJU Int., 2012,Oct; 33 (3): pp. 315-317.
6. Toropova V.А., Petrenko S.N. “NLS-diagnostics of prostate gland diseases “ // Collection of scientific works of the Institute of Practical Psychophysics “Actual problems of NLS-diagnostics”. Volume I. М: Katalog, 2006, p. 41-46.
