М. Zuckermann, A. Mozgen, C. Lerol
University clinic “RECHTS DER ISAR”
In order to evaluate informativity of three-dimensional virtual NLS-imaging method in revealing of distal bile-excreting ducts and major duodenal papilla tumors the authors carried out retrospective analysis of 34 patients’ clinical records, who were admitted to the clinic with symptoms of biliary obstruction. Control group consisted of 30 patients without symptoms of gastrointestinal tract diseases, the 2nd group – 20 patients with major duodenal papilla tumor, the 3rd group – 14 patients with tumorous affection of distal bile-excreting ducts. The authors carried out a comparative analysis of various instrumental methods and research methods informativity (two-dimensional and three-dimensional NLS-graphy, computed tomography, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Informativity of NLS-image three-dimensional reconstruction method was higher than informativity of two-dimensional NLS-study in diagnostics of distal bile-excreting ducts and major duodenal papilla tumors (accuracy 96,9 against 79,4% and 95,5 against 83,9% correspondingly).
Introduction
Technological innovations of the recent years in equipment for non-linear diagnostics and software resulted in cardinal extension of NLS-research application area and improvement of images quality. One of the promising directions for the development of NLS-diagnostics is a mode of multidimensional virtual reconstruction of an NLS-image, allowing to visualize crosscuts and anatomical reconstruction of a researched area, which remain invisible during application of two-dimensional scanning only. This method offers the possibility of data manipulating, using rotation and zooming, rendering true anatomy of organs in a direct projection. Three-dimensional NLS-scanning has a certain technical and practical advantages in visualization of anatomical and pathological structures in comparison with two-dimensional visualization. The method allows to make a crosscuts of acquired image, for example frontal ones, or to isolate separate areas in Fast Vision mode. It makes possible to see an internal structure of a parenchymatous organ, and if there are areas of affection inside the investigated region, an operator can isolate and zoom in areas of a parenchyma and thus see intratissual growths – in NLS-ultramicroscanning mode. Spectral-entropic analysis (SEA) mode allows to define morphological character of a researched area by comparison of spectral similarity with etalon processes.
According to T. Guseva et al., three-dimensional NLS is better in investigation of anatomical motion of hepatic vessels and biliary ducts, than standard two-dimensional NLS-investigation.
A. Schvack in his work evaluates practicability of three-dimensional NLS-scanning application in work with patients suffering from obstructive diseases of bile-excretory system. After comparison of three-dimensional NLS-scanning with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography it was noted that three-dimensional NLS-scanning has almost the same efficiency and informativity in evaluation of biliary system pathology as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Modern and accurate diagnostics of pancreas diseases, gall bladder and biliary ducts, without which it is impossible to carry out proper treatment, is regarded as one of the most important objectives in a modern gastroenterology. Three-dimensional NLS-imaging method still has not found a wide spreading in gastroenterology. Mainly it is applied for differential diagnostics of focal lesions.
In a group of patients with tumorous affection of bilepancreaticoduodenal region organs, neoplasms of major duodenal papilla are registered in 12% – 20% and comprise approximately 5% of all gastrointestinal tract tumors. A tumor may grow from epithelium of a common bile duct, pancreatic duct or mucous tunic of duodenum. Major duodenal papilla cancer crows relatively slow and metastasizes rather late. Most often a tumor represents an adenocarcinoma at microscope research. Location of a tumor at this level promotes relatively early appearance of jaundice. At major duodenal papilla cancer a jaundice is either of wave-form (without complete normalization of bilirubin level), or intermittent (with increasing of bilirubin and short-term period of decreasing to a normal level). Tumors of major duodenal papilla ulcerate quite quickly. This fact promotes infiltration of an infection from duodenum to biliary ducts and pancreatic ducts. Inflammatory component at major duodenal papilla cancer leads to a serious diagnostic mistakes.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy and three-dimensional NLS have a significant importance in diagnostics of major duodenal papilla tumors. Endoscopic picture of the cancer at late stages is quite typical: tuberiferous tumor of red or crimson color, occupying a part or whole major duodenal papilla.
Due to similar density values of major duodenal papilla cancer and surrounding bile, application of computed tomography cannot visualize this lesion, especially when a tumor is small and bile and pancreatic ducts are not dilated. But CT is more precisely, in comparison with standard two-dimensional NLS-study, identifies a side and reason of extrahepatic biliary obstruction. At major duodenal papilla cancer CT shows rupture of common bile duct and major pancreatic duct without any signs of these manifestations combination with tumorous affection. When positive contrast is used, a small defect in an area of major duodenal papilla is seen in duodenum lumen.
However a node with smooth contours in duodenum lumen can be registered at protrusion of bile duct distal part into duadenum lumen.
Tumors of extrahepatic bile ducts hold a significant place among malignant tumors of bilepancreaticoduodenal region organs. There are nodular, infiltrative and papillary forms of cancer. At infiltrative form of cancer complete obstruction of bile-excretory ducts happens later, metastases are registered more often and possibility of radical surgery fulfillment is lesser. The most positive prognosis is made at papillary cancer.
Jaundice in this group of patients is more intense and persistent. In 30% of patients cancer combines with choledocholithiasis.
In all diagnostically not specified cases in is recommended to apply 3D NLS with SEA to make a clear diagnosis and exclude obstructive jaundice. Diagnostic accuracy of 3D NLS with SEA is 89.4% – 97.8% (at comparison with data acquired during surgical operation or autopsy). The method is considered more efficient than ultrasound research, CT or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Moreover method of 3D NLS-ultramicroscanning allows to carry out a biopsy.
Besides, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, just like other endoscopic interventions, is not completely safe and related to a broad spectrum of complications. Serious complications, which can develop due to endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography application, are responsive pancreatitis, hemorrhage from areas of major duodenal papilla, gall bladder, bile-excretory and Wirsung ducts, perforation of duodenum and bile ducts, infectious complications (purulent angiocholitis first of all). According to some authors, frequency of responsive pancreatitis development after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography was 7% – 40%. Differing from ERCPG, NLS-investigation is absolutely safe and harmless.
Surgical intervention is the only method of treatment at this pathology. It is considered reasonable to settle all diagnostic questions regarding obstructive jaundice revealing and prepare a patient for surgical intervention in 10 days since the moment of its appearance. Moder diagnostic can be considered a way of treatment literally. Late surgical operations in this case lead to high rates of lethal outcome. Unnecessary surgical intervention should be avoided in patients with disseminated tumor, however it is important to select a group of patients for which radical surgery is possible.
At the present moment none of clinical and hardware investigation methods can properly solve all these objectives alone. Results of roentgen diagnostics of cancerous affection are far from perfect. It is important to define a role of not separate methods of clinical and hardware investigation, but of their combination.
The objective of this work is a study of three-dimensional NLS-image reconstruction in modern diagnostics of distal bile-excreting ducts and major duodenal papilla tumors.
Material and methods of investigation
We carried out a retrospective analysis of 34 patients’ clinical records, who were admitted to the clinic with symptoms of biliary obstruction. The first (control) group consisted of 30 patients administered to residential treatment without symptoms of gastrointestinal tract diseases. The second group – 20 (of 34) patients with major duodenal papilla tumor, the third group – 14 (of 34) patients with tumorous affection of distal bile-excreting ducts. In patients of the second group we registered clinical signs of pancreas affection two times more often. Continuance of symptoms in both groups was from 3 days to 4 months (Table 1).
Table 1. Parameters of patients in groups
|
Parameters |
1st group (n = 30) |
2nd group (n = 20) |
3rd group (n = 14) |
|
Average age of patients, years Diseases of stomach and duodenum (%) Cholecystectomy in past medical history At admission, symptoms of (%): juandice acute pancreatitis |
42-72 – –
– – |
40-77 100,0 30,0
50,0 30,0 |
60-74 85,7 43,0
43,0 14,0 |
At the first stage all patients were subjected to routine ultrasound examination of hepatobiliary system organs. Further on, in order to specify a nosological for of a disease, we used method of three-dimensional virtual NLS-reconstruction of an image and other hardware and laboratory researches (in accordance to medical and financial standards for this nosological type of a disease).
Ultrasound examination was carried out with Acuson Sequoia 512 (Siemens, Germany) device, with multifrequency curvilinear transducer (2.5 – 6 MHz). Three-dimensional NLS-graphy was carried with Metatron-4025 (IPP, Russia) system with 4.9 GHz frequency generator and “Metapathia GR Clinical” software allowing to carry out three-dimensional virtual rendering of an object. Three-dimensional reconstruction was possible because of integrated into Metatron system specialized computer and mathematical program for NLS-information processing and virtual rendering of an image in various formats. The acquired data was processed with programs of interactive multidimensional visualization – 4D Tissue. These programs allow to get images with shaded surface and transparent layers.
We also used DeepVision mode, which can make transparent external walls of gall bladder wall and biliary ducts and thus to help to monitor and evaluate deep structures of cavitary lesions, normally hidden by the external layers.
To carry out more detailed evaluation of revealed changes we used the following functions: rotation of an image, allowing to rotate three-dimensional array in any projection for accurate perception of a shape and a surface of a scanned object; segmentation of an image (Fast Vision), allowing to select area of interest from the main image and remove screening structures. Modes of rotation, segmentation and multiplanar image scanning help to improve significantly evaluation quality of all analyzed signs with their following analysis, as the addition to transparency of multidimensional image on/off mode. Multiplanar image scanning mode with step-by-step visualization and evaluation of all signs in a researched area allows to specify a localization of an object and evaluate in details all analyzed signs with simultaneous scanning in three planes in a selected crosscut. The optimal procedure is a consecutive application of all available three-dimensional image rendering modes for studying of every patient.
Acquired 3D NLS results were compared to data of a standard ultrasound research, CT, fiberoptic gastroduodenoscopy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and surgery findings.
Results of the study and discussion
Because of evidence based medicine principles introduction into practice, requirements to hardware diagnostic methods have increased. Accurate information about presence of pathological changes in surrounding tissues and organs, related to biliary obstruction, must be provided. Application of three-dimensional virtual NLS-diagnostics modes allows to specify accurately the amount of tumorous affection, its interrelation with surrounding vessels and bile ducts, intensity of invasion into surrounding tissues.
NLS-symptoms of tumorous lesion included direct symptoms, when tumor itself is visualized – a solitary nidus of heterogeneous structure, with different (decreased mainly) chromogeneity, with a line of demarcation between a tumor and surrounding normal tissue. Application of ultrasound research methods usually visualizes tumors of 10 mm and larger. Three-dimensional NLS-ultramicroscanning mode with spectral-entropic analysis allows to diagnose tumors sized 1mm and lesser.
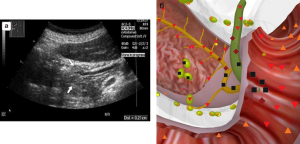
Pic. 1. Patient R., 62 years old. A tumor of major duodenal papilla, growing into a lumen of a duodenum. Stenosis of a distal part of a common biliary duct. Thickening of walls and increasing of chromogeneity of a major duodenal papilla. А – visualization in B-mode of two-dimensional echography. B – visualization in NLS multiplanar multidimensional image reconstruction mode.
Tumors of distal bile-excreting ducts and major duodenal papilla due to tumorous invasion, circular squeezing and growth into a lumen of a duct may cause an obstruction. At the same time indirect symptoms of biliary obstruction are registered: dilation of proximal areas of bile ducts; enlargement of gall bladder; development of hepatic changes, typical for hepatic secretory obstruction. At accompanying obstruction of main pancreatic duct directly at the point of transition to ampoule, a dilation of a duct is detected distal to obstruction level.
In the second group of 20 patients with major duodenal papilla tumor in 6 patients we registered a growth of a tumor into a lumen of a duodenum, in 14 patients – into a lumen of a common bile duct. Precise diagnostics with ultrasound research was done in 19 patients (in 1 patient with growth of a tumor into a lumen of a common bile duct ultrasound found a tumor of pancreatic head with metastases into distal parts of a common bile duct).
A direct symptom of major duodenal papilla tumor is revealing of a space-occupying process in its projection. At growing of a neoplasm into a lumen of a duodenum (n = 6), we detected dilation and tortuosity of a common bile duct distal part and significant thickening of a papilla’s walls, echogeneity of which was decreased mainly. There was no sign of significant dilation of a common bile duct (diameter 0.65 – 1 cm). Also there was no dilation of intrahepatic bile ducts and a major pancreatic duct. Presence of a tumor was confirmed by fiberoptic gastroduodenoscopy with the following histological research. In 4 patients we revealed a glandular cancer, in 2 – adenocarcinoma.
Application of three-dimensional virtual NLS-diagnostics allowed to increase sensitivity up to 100%, specificity – up to 97% (in 1 patient- false-positive result) in comparison with a standard ultrasound research (see Table 2). Application of CT at the absence of a significant dilation of bile-excretory ducts had lesser diagnostic value (sensitivity – 66.7%, specificity – 93.5%).
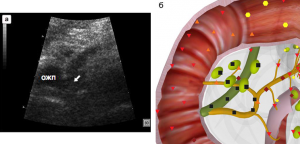
Pic. 2. Patient R. 66 years old. A tumor of a major duodenal papilla, growth into a lumen of a common bile duct, dilation and increasing of chromogeneity of a common bile. A – visualization in B-mode of two-dimensional echography. B – visualization in NLS-multidimensional image reconstruction mode.
Table 2. Informativity (%) of ultrasound and NLS-diagnostics in revealing of major duodenal papilla pathology
|
Type of tumor growth
|
Ultrasound diagnostics |
Three-dimensional NLS-graphy |
||||
|
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
Accuracy |
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
Accuracy |
|
|
Into a lumen of a duodenum Into a lumen of a common bile duct |
66,7 78,5 |
86,7 84,5 |
88,9 91,3 |
100,0 92,8 |
97,0 98,1 |
97,8 96,2 |
At growing of a tumor into a lumen of a common bile duct (n = 14), in a lumen of a common bile duct (diameter 0.9 – 1.6 cm) in projection of a major duodenal papilla we detected a neoplasm of various chromogeneity, obstructing a lumen of the duct. Glandular cancer (4 patients) was characterized by a neoplasm of increased chromogeneity (5-6 points at Fleindler’s scale), adenocarcinoma (10 patients) by a neoplasm of lesser chromogeneity (below 5 points).
In patients of the second group intrahepatic ducts were dilated in 30% of cases. Diameter of intrahepatic bile ducts varied from 0.2 to 0.5 cm, diameter of a common bile duct was of 0.65 – 1.6 cm. We also registered increasing of bile duct surface up to 51 sq. cm. (12 – 51 sq. cm.). Concomitant concretions in a gall bladder were revealed in 20% of cases, choledocholithiasis – in 10% of cases. Dilation of a common pancreatic duct was revealed in 40% of patients, diameter of the duct varied from 0.2 cm to 0.7 cm.
When we chose an adequate area for application of three-dimensional NLS-reconstruction and applied a combination of various modes of acquired image post-processing, specificity, sensitivity and accuracy of diagnostics increased greatly (see Table 3).
Table 3. Informativity (%) of various methods and modes of diagnostics.
|
Methods and modes |
2nd group |
3rd group |
|
Ultrasound scanning: sensitivity specificity accuracy Three-dimensional NLS-graphy: sensitivity specificity accuracy Fiberoptic gastroduodenoscopy: sensitivity specificity accuracy CT: sensitivity specificity accuracy endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: sensitivity specificity accuracy |
75,0 95,6 89,4
95,0 97,7 96,9
95,0 97,8 96,9
68,4 97,7 87,6
100,0 100,0 100,0 |
71,4 96,1 90,9
92,8 96,1 95,5
85,7 96,1 95,5
83,3 98,0 95,4
100,0 100,0 100,0 |
Especially obvious advantages of three-dimensional NLS-graphy over a standard ultrasound research can be seen at revealing of major duodenal papilla tumor sized less than 10 mm.
In order to carry out differential diagnostics and to confirm results of an ultrasound research, in 8 cases from this group we applied endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, which allowed to specify histological structure of a tumor, but in 12.5% this procedure was accompanied by complications in a form of acute pancreatitis development.
In all our studies (of 14 patients) a direct signs of a common bile duct tumorous affection were local lesion of the duct’s wall (of various length) with disintegration of layer-by-layer structure of a tissue and hyperchromogenic growth in a lumen of the duct. Visualization of affected wall at 3D NLS was significantly improved by following processing of an acquired image.
Tumors of distal part of a bile duct were accompanied by significant increasing of gall bladder size. Surface area of gall bladder varied from 32 sq.cm. to 57 sq.cm. Dilation of intrahepatic ducts was registered in 57% of patients. Diameter of intrahepatic bile ducts ranged 0.2-0.8 cm, of a common bile duct – 0.7 – 1.7 cm. Concomitant concrements in a gall bladder were revealed in 14.3% of patients. Localization of a tumor in intramural part of a common bile duct caused an obstruction of major pancreatic duct entrance, which was dilated in 71.4% of patients. Diameter of major pancreatic duct varied from 0.1 to 0.8 cm.
Informativity of three-dimensional NLS-study exceeded informativity of ultrasound research (see Table 3).
In one patient a tumor of pancreatic head with metastases into a distal part of a common bile duct was diagnosed erroneously. A correct diagnosis was made during surgical intervention.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography was applied with a view of treatment and diagnosing in 10 patients, but in 20% of patients in was accompanied by acute pancreatitis development.
Laboratory diagnostics of a common bile duct distal part and major duodenal papilla cancer show increasing of total bilirubin level (because of direct and indirect fractions), alkaline phosphatase, aminotransferase and accelerated ESR. Level of СА-19-9 oncomarker was increased in 42% of patients and it was related to major duodenal papilla tumor growth into a lumen of a common bile duct.
Thus non-invasive methods of diagnostics, including one of the net trends – three-dimensional virtual NLS-diagnostics method, provide increasingly accurate diagnostic information. Application of this technology allows not only to decrease a risk of various complications development, related to invasive diagnostics application (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography), but in some cases to exclude application of duplicate radiological methods (CT) and to optimize diagnostic algorithm of patients examination.
Reliability of ultrasound research in revealing and differentiation of bile excretory ducts is quite high, but sonographic signs, used to fulfill proper differential diagnostics, are far from perfect. The important moment is the application of modern diagnostics equipment and new research technologies.
Three-dimensional virtual NLS-diagnostics mode offers accurate presentation of a shape, surface and structure of a researched neoplasm. From a clinician’s point of view such combined information is very essential, because it makes possible to evaluate interrelation of organs and pathological changes in them.
Dealing with a problem of bile excretory ducts differential diagnostics by means of SEA with three-dimensional visualization is regarded as quite promising way, permitting to optimize treatment and diagnostic processes, decrease a number of inefficient researches, cut application rate of expensive invasive methods in algorithm of this category of patients investigation.

Pic. 3. Patient F., 67 years old. NLS-ultramicroscanning. A tumor of a distal part of a major duodenal papilla.
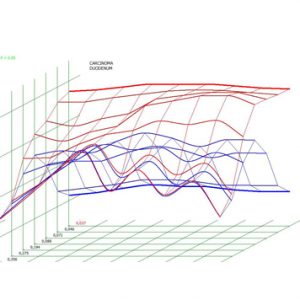
Pic. 4. Spectral-entropicanalysis. Cancer of a major duodenal papilla (D=0,037).
The following aspects are important for acquisition and efficient evaluation of three-dimensional image during NLS-research:
– an operator must be proficient in NLS-diagnostics principles, anatomical picture of investigated area, nosological forms and clinical course of diseases typical for investigated organs;
– methodological accuracy of NLS-investigation of organs in 3D mode;
– chhosing of a proper area for three-dimensional reconstruction of NLS-image;
– consecution of various methods of NLS-image post-processing and their combination;
– application of ultramicroscanning with SEA for evaluation of researched tissues affection micronidi and when there is no adequate interpretation of these affections character.
After therapists master this type of diagnostics, three-dimensional non-linear reconstruction of an image method will have prospects for application not in large clinics only, but at early stages of medical treatment.
Conclusion
1. Three-dimensional virtual NLS-diagnostics method makes possible to increase informativity in revealing of direct and indirect symptoms of biliary obstruction.
2. Ultramicroscanning mode with SEA is the most optimal for revealing of lesser space-occupying masses and identifying of their character.
3. Application of three-dimensional virtual NLS-reconstruction of an image method provides early revealing of biliary obstruction reasons, reduces the price of patients investigation thanks to more rational application of expensive and invasive diagnostic methods.
4. Three-dimensional virtual NLS-diagnostics allows to evaluate results of treatment maneuvers.
References
1. Thomas R., Dolores H. Interactive acquisition, analysis and visualization of sonographic volume date // Int. J. Imaging Technol. 1997. V. 35. P.40–47.
2. Campani R., Bottinelli O., Calliada F., Coscia D. The latest in ultrasound: three-dimensional imaging. Part II // Eur. J. Radiol. 1998. V. 27. Suppl. 2. P. S183–S187.
3. Rohling R.N., Gee A.N., Berman L. Automatic registration of 3-D ultrasound images // Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1998. V. 24. № 6. P. 841–854.
4. Sanches J.M., Margues J.S. A multiscale algorithm for three-dimensional free-hand ultrasound // Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002. V. 28. № 8. Р. 1029–1040.
5. Wagner S., Gebel V., Bleck J.M., Manns M.P. Clinical application of three-dimensional sonography in hepatobiliary disease // Bildgebung. 1994. V. 61. № 2. P. 104–109.
6. Lee H.J., Choi B.I., Han J.K. et al. Three-dimensional ultrasonography using the minimum transparent mode in obstructive biliary diseases: early experience // J. Ultrasound Med. 2002. V. 21. № 4. P. 443–453.
7. Sherlock S., Dooley J. Diseases of liver and bile ducts: Practice directions, 1999. 864 p.
8. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery: the Biological Basis of Modern Surgical Practice. 16th ed. / Ed. By Beauchamp R.D., Evers B.M., Townsend C.M. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2001. P.1076–1143.
9. Masci E., Mariani A., Curioni S., Testoni P.A. Risk factors for pancreatitis following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a metaanalysis// Endoscopy. 2003. V. 35. № 10. P. 830–834.
10. Friedlend S., Soetikno R.M., Vandervoort I. et al. Bedside scoring system to predict the risk of developing pancreatitis following ERCP // Endoscopy. 2002. V. 34. № 6. P. 483–488.
11. Tokar S.P., Davydova А.S., Guseva Т.L., Gusarov V.I., Khabibullina Z.F., Pugacheva L.S. Non-linear computed diagnostics and problems of hepatopancreoduodenal region pathologies // Collection of scientific works of the Institute of Practical Psychophysics “Actual aspects of NLS-diagnostics”. Tome I. М.: Katalog, 2006, p.. 77-88.
12. Guseva Т.L., Khabibullina Z.F., Kharlamov U.S. Application of NLS-diagnostics at extrahepatic bile ducts diseases // 3D computed NLS-graphy: Collection of scientific works / Editor V.I. Nesterov. – М.: Publishing house Prospekt, 2012, p.18-20.
13. Shvack А.Y., Nesterov V.I., Ogluzdina N.L. Certain aspects of NLS-diagnostics of hepatic nidal pathology // Collection of scientific works of the Institute of Practical Psychophysics “NLS-technologies in medicine – prospects of development». Tome III. М.: Katalog, 2010, p. 13-19.
